Questions? Comments? Please contact Dr. Phillip McClean or Christina Johnson.
|
| OVERVIEW |
| Flythrough Tour |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| MOLECULAR PROCESSES |
| Transcription |
| Regulated Transcription |
| mRNA Processing |
| mRNA Splicing |
| Translation |
| Lac Operon |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| CELLULAR PROCESSES |
| Protein Trafficking |
| Protein Modification |
| Protein Recycling |
| Insulin Signaling |
| Constitutive Secretion |
| Regulated Secretion |
| Mitochondrial Protein Transport |
| Mitosis |
| Meiosis |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| CELLULAR ENERGY CONVERSION |
| Atp Synthase (Gradients) |
| Electron Transport Chain |
| Photosynthesis (Light Reaction) |
| Photosystem II |
| Glycolysis (Overview) |
| Glycolysis (Reactions) |
| Citric Acid Cycle (Overview) |
| Citric Acid Cycle (Reactions) |
| Energy Consumption |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| NDSU Virtual Cell YouTube |
| MCBE Home |
| Virtual Cell |
| WWWIC Home |
| Funding & Credits |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| HOME > MITOCHONDRIAL PROTEIN TRANSPORT > ADVANCED LOOK > 1.) CYTOSOL > 2.) MATRIX |
| Mitochondrial Protein Transport : Advanced
Look --> 2.) Matrix
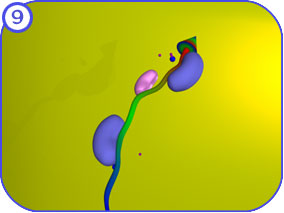
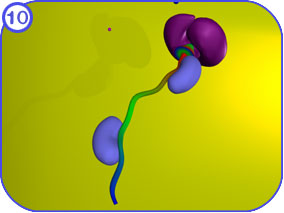
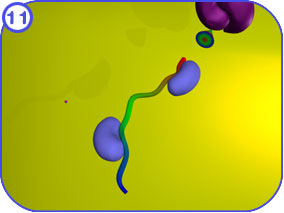
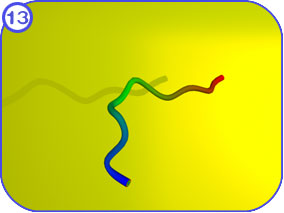
The final steps of protein transport int the mitochondria occur in the matrix space. Clicking on each of the thumbnail images will bring up a larger, labeled version of the described scene. To see the Flash movie for the following sequence of images, click here. |

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.