Questions? Comments? Please contact Dr. Phillip McClean or Christina Johnson.
|
| OVERVIEW |
| Flythrough Tour |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| MOLECULAR PROCESSES |
| Transcription |
| Regulated Transcription |
| mRNA Processing |
| mRNA Splicing |
| Translation |
| Lac Operon |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| CELLULAR PROCESSES |
| Protein Trafficking |
| Protein Modification |
| Protein Recycling |
| Insulin Signaling |
| Constitutive Secretion |
| Regulated Secretion |
| Mitochondrial Protein Transport |
| Mitosis |
| Meiosis |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| CELLULAR ENERGY CONVERSION |
| Atp Synthase (Gradients) |
| Electron Transport Chain |
| Photosynthesis (Light Reaction) |
| Photosystem II |
| Glycolysis (Overview) |
| Glycolysis (Reactions) |
| Citric Acid Cycle (Overview) |
| Citric Acid Cycle (Reactions) |
| Energy Consumption |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| NDSU Virtual Cell YouTube |
| MCBE Home |
| Virtual Cell |
| WWWIC Home |
| Funding & Credits |
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| HOME > ETC > ADVANCED LOOK > 1.) NADH > 2.) CYTOCHROME b-c1 > 3.) CYTOCHROME OXIDASE > 4.) ATP SYNTHASE |
| ETC:
Advanced Look -->
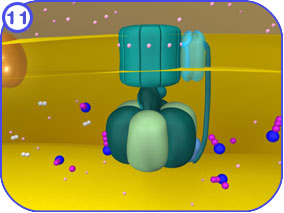
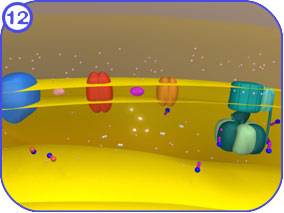
4.) ATP Synthase
ATP synthase is considered a part of the electron transport chain, but it is not involved in the transport of electrons. ATP synthase uses the proton gradient created by the ETC to synthesize ATP. Clicking on each of the thumbnail images will bring up a larger, labeled version of the described scene. To see the Flash movie for the following sequence of images, click here.
|

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.